What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)? The Basics Every Business Should Know
IT asset management (ITAM), What is it and how it helps businesses keep track of their technology, save money, stay secure.
As businesses grow with more sales, more money, and more employees, their need for technology expands too. More people means more computers, servers, software, and a bigger network to support daily operations. As companies take on tasks like HR or data management in-house, IT assets can quickly pile up.
IT Asset Management (ITAM) helps businesses stay organized by tracking and managing their technology resources from purchase to retirement. It ensures your assets are used efficiently, helps avoid unnecessary costs, and keeps your business compliant with software licenses.
What is an IT Asset?
An IT asset encompasses any hardware, software, or information that holds value for an organization. This includes physical devices like computers and servers, software applications and licenses, and critical data integral to business operations.
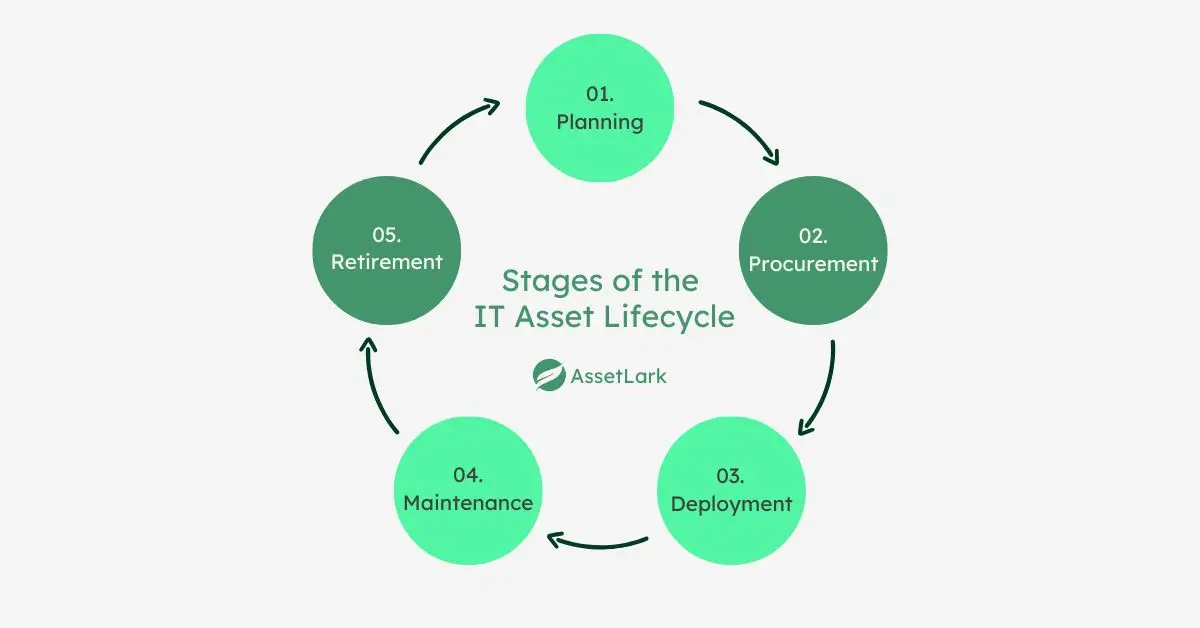
Each IT asset undergoes a lifecycle with distinct stages:
- Planning: Identifying the need for an asset and strategizing its acquisition.
- Procurement: Acquiring the asset through purchase or licensing.
- Deployment: Installing and integrating the asset into the organization's IT environment.
- Maintenance: Regularly updating and servicing the asset to ensure optimal performance.
- Retirement: Decommissioning the asset when it's no longer useful or efficient.
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)?
ITAM is the process of tracking and managing an organization's IT assets—like hardware, software, and digital resources—from acquisition to disposal. It ensures assets are properly used, maintained, upgraded, and retired at the end of their lifecycle, helping businesses stay efficient, reduce costs, and remain compliant.
Types of IT asset management?
ITAM can be categorized into 3 primary types based on the nature of the assets being managed within an organization's IT infrastructure:
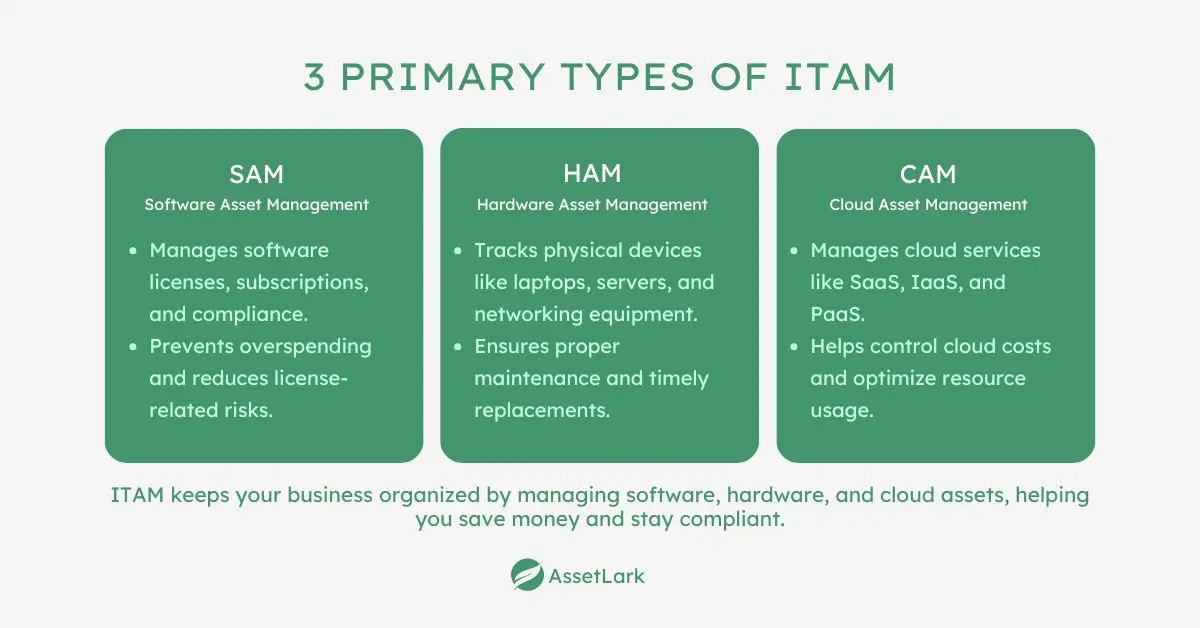
1. Software Asset Management (SAM)
SAM focuses on tracking and managing an organization's software applications, licenses, and subscriptions. It ensures that software is properly licensed, up to date, and compliant with legal requirements.
SAM helps prevent issues like over-licensing, under-licensing, and unauthorized software use, while also optimizing software investments by eliminating unused tools and ensuring cost-effective resource allocation.
Examples of Software Assets:
- Software assets include tools like Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce for productivity and collaboration.
- Security software such as Norton Antivirus and development tools like Visual Studio and GitHub also fall under this category, along with operating systems like Windows and database tools like Oracle and MySQL.
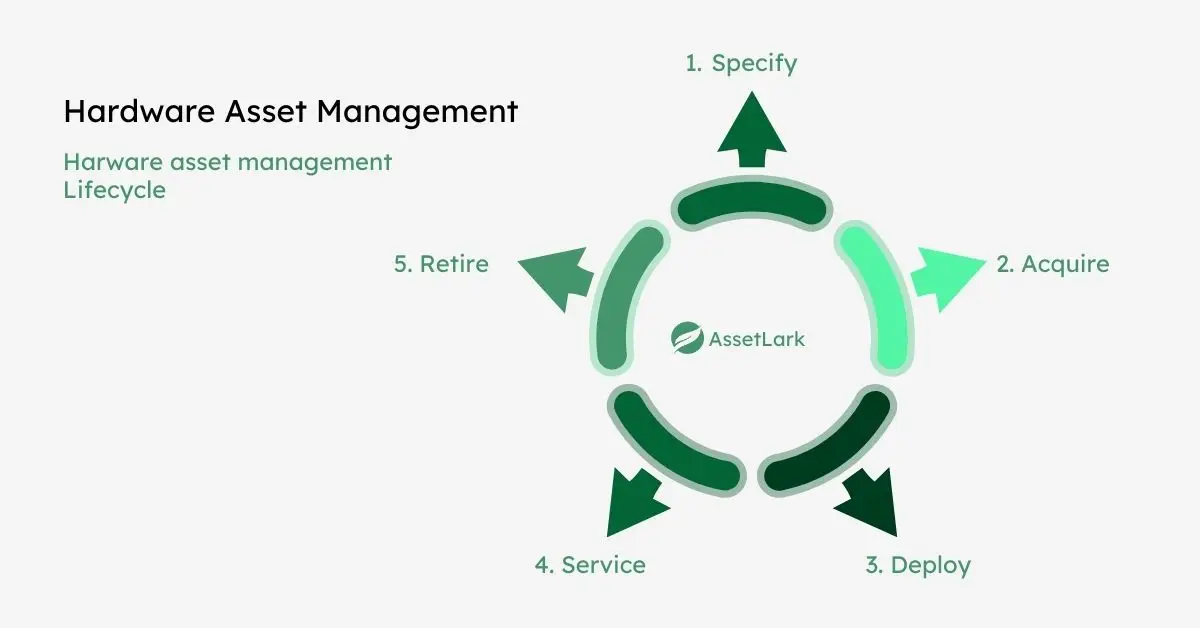
2. Hardware Asset Management (HAM)
HAM involves the management of physical IT equipment used within an organization. This includes tracking the location, condition, and lifecycle of devices like computers, servers, and networking equipment.
HAM ensures that hardware is properly maintained, secured, and replaced when necessary, helping businesses extend the lifespan of their equipment while preventing unnecessary purchases and asset loss.
Examples of Hardware Assets:
- Hardware assets cover physical devices such as laptops, desktops, servers, and storage devices used for operations.
- It also includes networking equipment like routers, switches, and firewalls, as well as printers, scanners, and mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
3. Cloud Asset Management (CAM)
CAM focuses on managing cloud-based resources and services, such as SaaS (Software as a Service), IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), and PaaS (Platform as a Service). It helps organizations monitor cloud usage, control service costs, and ensure compliance with service agreements. CAM also ensures cloud resources are optimized, preventing over-subscription or underutilization of services.
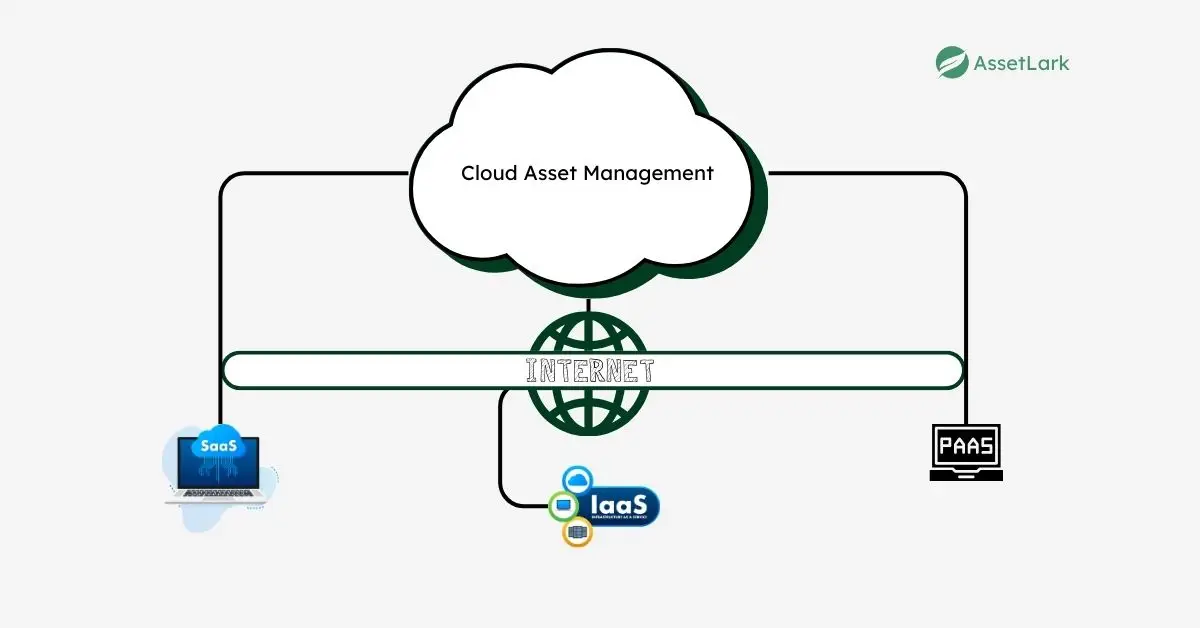
Examples of Cloud Assets:
- Cloud assets include SaaS tools like Zoom, Slack, and Dropbox, IaaS platforms such as AWS and Microsoft Azure, and PaaS services like Google Cloud Platform and Heroku.
- Cloud storage services like Google Drive and security platforms like Cloudflare are also part of cloud asset management.
Learn more about the types of asset management.
Key Components of IT Asset Management:
- Asset Tracking: Monitoring asset location, usage, and condition.
- Inventory Management: Creating a centralized record of all IT assets, including hardware, software, and cloud services.
- Lifecycle Management: Managing assets from procurement to retirement.
- License Management: Ensuring software licenses are properly tracked, compliant, and optimized.
- Security and Risk Management: Protecting assets from unauthorized use and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Cost Management: Controlling expenses by optimizing asset usage and preventing unnecessary purchases.
- Asset Allocation: Assigning IT assets to employees, teams, or departments based on business needs.
- Asset Onboarding: Deploying IT assets for new hires or projects, ensuring they are pre-configured and ready for use.
- Asset Offboarding: Reclaiming IT assets during employee exits or project completions while securing data.
- Asset Booking: Managing asset reservations and loaner equipment to avoid conflicts and ensure availability.
- Compliance Management: Ensuring adherence to software licenses, vendor agreements, and regulatory standards.
- Maintenance and Optimization: Performing regular maintenance, updates, and performance checks to extend asset life.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing insights on asset performance, utilization, and financial impact.
The IT asset management process
1. Inventory Assets
Inventory assets refer to the complete and organized listing of all IT resources within an organization, including hardware, software, cloud services, and data assets. This process involves recording key details about each asset, such as its type, location, owner, and purchase information, to ensure full visibility and control over the IT environment.
Objective of Inventory Assets in ITAM:
- Provide a clear view of all IT assets, their locations, and usage.
- Ensure software licenses are properly tracked and compliant with vendor agreements.
- Reduce risks by identifying unauthorized or unmonitored devices.
- Prevent duplicate purchases and underutilized assets.
- Maintain up-to-date asset records for better planning and reporting.
Example: Your company documents all laptops, servers, and software licenses, tagging each with unique identifiers and recording key details to ensure visibility across departments.
2. Track the complete IT asset lifecycle
Tracking the complete IT asset lifecycle involves managing an asset from its initial request through its retirement and disposal.
Objective of Tracking the IT Asset Lifecycle:
- Maintain a clear record of asset status and history.
- Ensure proper decommissioning and data protection.
- Maximize asset value throughout its lifecycle.
- Adhere to regulatory and licensing requirements.
3. Asset Tracking
Asset tracking in IT Asset Management (ITAM) involves the continuous monitoring of IT assets throughout their lifecycle using technologies such as GPS, barcodes, and RFID.
Components of Asset Tracking
- Check-in/Check-out Management: Track asset movement and user assignments.
- Unique Identifiers: Use barcodes, RFID tags, or asset tags for easy identification.
- Location Tracking: Monitor asset locations, especially for mobile devices and hardware.
- License Tracking: Ensure all software licenses are valid and compliant
Key Objectives of Asset Tracking:
- Maintain a clear view of asset location, ownership, and usage.
- Ensure assets are assigned to the correct users and departments.
- Monitor software licenses, warranties, and service agreements.
- Prevent unauthorized use and reduce asset loss or theft.
- Optimize asset utilization and avoid unnecessary purchases.
4. Maintenance and Optimization
Maintenance and optimization involve regularly managing and servicing IT assets to keep them functional, secure, and efficient throughout their lifecycle.
Key Maintenance and Optimization Activities:
- Software Updates: Regularly updating software for security patches and feature improvements.
- Hardware Servicing: Performing physical maintenance like cleaning, part replacements, and diagnostics.
- Performance Optimization: Monitoring asset performance and optimizing configurations.
- Upgrades and Repairs: Implementing necessary hardware upgrades and repairs.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Ensuring critical data is backed up during maintenance.
Objectives of Maintenance and Optimization:
- Prevent wear and tear with regular maintenance.
- Reduce disruptions with proactive servicing.
- Keep assets running at peak efficiency.
- Apply software patches and updates on time.
- Maximize productivity from existing assets.
5. Keep tabs on the metrics that matter
Tracking key metrics in IT Asset Management means monitoring asset performance, usage, and compliance to improve business decisions.
Important Metrics to Track:
- Number of Active Assets: Total hardware, software, and cloud assets in use.
- Utilization Rate: How frequently assets are used compared to availability.
- Software License Compliance: Number of valid vs. expired software licenses.
- Asset Downtime: Frequency and duration of asset unavailability.
- Maintenance Frequency: How often assets require servicing.
- End-of-Life (EOL) Assets: Assets reaching retirement or requiring replacement.
Key Objectives:
- Measure asset health, efficiency, and productivity.
- Track total cost of ownership (TCO) and spending patterns.
- Ensure proper licensing and security standards.
- Monitor how assets are being used and reallocate resources effectively.
- Identify underperforming or outdated assets.
Benefits of IT asset management
Effective IT Asset Management (ITAM) offers significant advantages that help organizations make smarter business decisions, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency. Here are the key benefits:
1. Centralized Asset Database/Inventory
A single, organized asset database simplifies asset tracking and management. By consolidating all asset information in one place, organizations reduce inaccuracies, prevent disorganization, and gain a clearer view of their IT landscape. This allows for easier identification of assets needing upgrades, replacements, or optimization.
"You can't manage what you can't measure." – Peter Drucker
2. Optimized Asset Utilization
ITAM ensures resources are used efficiently, minimizing waste and reducing unnecessary expenses. Real-time data on asset health and performance helps organizations maximize productivity while preventing resource underutilization.
3. Software License Compliance
ITAM helps businesses stay compliant with software license agreements by continuously monitoring software usage. This prevents legal risks, financial penalties, and disruptions due to non-compliance while ensuring the organization only pays for the software it actively uses.
4. Informed Decision-Making
Access to accurate asset data enables better strategic decisions. ITAM provides insights into asset performance, purchase history, and maintenance trends, helping organizations make data-driven choices for future IT investments and resource planning.
5. Risk Reduction and Security
Untracked or outdated assets can create security vulnerabilities. ITAM ensures all assets are accounted for, regularly updated, and properly maintained, reducing the risk of data breaches, unauthorized software use, and operational disruptions.
How to get started with ITAM?
- Start Where You Are – Assess your current ITAM processes, tools, and infrastructure to identify areas for improvement.
- Gain Executive Buy-In – Secure leadership support to ensure alignment with business goals and resource allocation.
- Form an ITAM Team to Pilot the Project – Assemble a team to run a small-scale pilot project before full implementation.
- Define Critical Assets – Identify key assets like high-value hardware, essential software, and cloud resources.
- Identify Cloud Resources – Include SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS services in your asset management scope.
- Select Flexible Tools That Grow With Your Business – Choose scalable ITAM tools that adapt to evolving business needs.
- Determine Asset Discovery and Integration Methods – Implement automated tools for asset discovery and ensure data integration.
- Use a Lifecycle-Based Approach – Manage assets from procurement to retirement for full lifecycle control.
- Continuously Track and Monitor Assets – Monitor assets regularly to avoid compliance risks and optimize usage.
- Gather Feedback and Continuously Improve – Collect stakeholder feedback to refine and improve ITAM processes.
How to Choose the Right IT Asset Management Software?
Choosing the right IT Asset Management (ITAM) software starts with understanding your needs. If you want to reduce costs, improve visibility, or move away from error-prone spreadsheets, ITAM software can help by centralizing asset data and preventing financial waste caused by lost or untracked assets.
Look for software that can scale with your business as it grows. Key features like asset discovery, license tracking, and automation help reduce manual work while keeping assets organized and compliant.
Ensure the software fits your requirements. Whether you need basic asset tracking or advanced tools for license management, cloud tracking, and IT infrastructure mapping, the right ITAM software should be flexible, collaborative, and capable of reducing risks and controlling costs.
Conclusion
A strong ITAM process improves security, prevents asset loss, and helps avoid unnecessary costs by providing clear visibility into how assets are used. With proper tracking, maintenance, and reporting, businesses can make better decisions about repairs, upgrades, and replacements.
In short, ITAM helps businesses save money, stay secure, and operate more smoothly. Investing in a solid asset management strategy ensures long-term efficiency and success.
AssetLark helps businesses keep track of their IT assets, manage them better, and make the most out of their technology resources.
